Essential Parts of the Website: How Does the Site Work From Within?
In this article, we will figure out what external parts of a website are there and what is the internal structure of the site. The site, like any program on your computer, looks clear and easy to navigate for the user. However, if a person who does not know special programming languages looks inside the site’s code, they won’t be able to separate the parts of the web page.
Fortunately, the visitors don’t need to see the skeleton of our site. They only access a beautiful external informative shell divided into several parts. Some parts of the homepage stay the same for all the site’s pages while others change. How does it work and why? Read on to find out what website parts should be always present and how to achieve their proper functioning from the inside.
Contents
What are the external parts of the website interface?
Header
It is located at the very top of any page on the site. It displays the name of the site, its brief description, and a picture (logo). The header is one of those parts of a website that presents the essence of the platform. It also includes the navigation menu, possibly a site search, and an account login panel (if there is a registration feature on the site).
You can place an advertisement in the form of a banner there or any other interactive pop-up depending on your preferences and specific needs. The header stays the same or almost the same for all the site’s pages.
Site Body
The site body can be called the main part of a website. All vital site information is located here. In contrast to the site header, there are no restrictions concerning what you should put here. The header must be brief and logically conclude the following information. Thus, the site body includes everything you want to share:
- articles and comments to them;
- advertisements;
- subscription plans;
- links to other parts of a website;
- videos and pictures;
- news and other content.
You have the complete freedom to post whatever you need here. The site body is among those website parts that you will change and upgrade from one page to another. It offers unique content that belongs to a specific URL.
Sidebar
The sidebar contains various information and navigation widgets (that you can create in WordPress), modules (Joomla). These components of a website include advertising, headings of articles, contacts in social networks, buttons for subscribing to a newsletter, logging into an account, various informers (calendar, clock, weather, exchange rates, etc.), site search, and site traffic counters.
There can be several sidebars, one on the left side and the other on the right or they may be doubled. It all depends on the site template and current website trends. Of course, the sidebar should be brief and offer a generalized list of what you can do on the site. It changes slightly depending on the site’s page.
Footer
Located at the very bottom of the site, the footer is a small note published after the main content. Site authors usually post various attendance counters, information on the rights to use the content posted on this site, or legal claims in this section. Footer belongs to those parts of a website layout that stay the same for all the pages.

Site structure for webmasters. What does the site consist of inside?
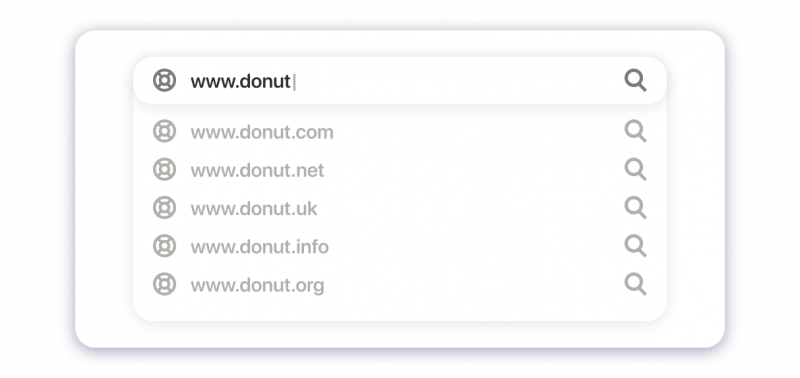
Domain name
It is the site’s address. You should enter this unique short name into the search field to find the platform on the web.
Hosting
A hosting is a special server that allocates space for storing site files, provides constant access to the Internet, and also takes the system load. Thus, it presents a physical place for storing the code and all internal structures.
Website Design
All parts of a website that you see upon opening the page make up the site’s design. All this is displayed on the site using ordinary images with different resolutions (.jpg or .gif) and special codes, drawn up in the CSS style language. All codes are stored on the hosting in one file, for example, “style.css”. This code is responsible on the site for the color, size, font, the place where this or that fragment or picture should be located.
HTML
When the design of the website parts is ready, the whole page is drawn using a special HTML language understood by the Internet browser. All design ideas are put together into one common code. Previously, the HTML code was written separately for each page, but now these principles have changed towards a more optimized approach.
JavaScript
This wonderful tool allows pages to be more dynamic. When a page is written exclusively in HTML, it is completely static. And thanks to JavaScript, we can enjoy things like pop-ups, slide-out bookmarks, sliding blocks, and much, much more.
Programming Language
Everything moves and everything changes. With the development of the site, the number of pages also grows, and it is very routine work to write and change the HTML code of each page. This is the reason why programming languages that automate the process of creating pages have emerged.
PHP has become the leader among all such languages for the web. Special CMS (WordPress, Joomla, Drupal) were created on its base allowing people without programming skills to easily create and manage separate components of a website and pages on the Internet. CMS integrates special algorithms that are written in files (page.php, index.php, functions.php, etc.) to optimize the site’s operation.
Database
When the site has a large amount of information, the easiest way is to store it in a database. With the help of the database, we can supplement, remove and change information about the website sections.
How does the site work?
Did you ever wonder what processes take place after you open the Internet browser and type in the domain name of the site? Here is a step by step explanation:
- The domain name tells the browser where the site is located.
- The browser, in turn, requests the hosting service to display the site.
- The hosting checks the form of the requested page. If it is just an HTML file, then it gives it to the browser, and if the site is written in a programming language, then the page formation process begins.
- According to the algorithm, an HTML page template is compiled and filled with data from the database that corresponds to the requested page.
- After the page is formed, it is sent to the browser.
- The browser code starts to load everything sequentially.
This process takes very little time, but if you have a slow Internet connection, you can notice the browser downloading the sections of a website you need.
Conclusion
Of course, if you are just a novice webmaster, then you may not yet quite understand everything. But everything comes with experience. You need to practice to gain experience. Take action, create your first website on Weblium, and good luck in this challenging business.
Complete the information in the comments, and feel free to ask your questions about the basic parts of a website. Finally, don’t forget to subscribe to our blog updates! Good luck!


